least count of brinell hardness tester|brinell hardness number chart : distribution Once the average indentation diameter is measured the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN or HBW) can be calculated using the following Brinell hardness test formula: Here, 1. F=Applied force, in kgf 2. D=diameter of indenter, in mm 3. d=diameter of . See more Spore test all sterilizers. You must test all sterilizers present in your sterilization area. If a sterilizer is not currently being used, or is considered a back-up, it still must be spore tested at least weekly.One question that’s commonly asked is how often you should clean autoclaves. These are delicate equipment that require constant care and maintenance. To increase the longevity of your autoclave, it’s best to clean them on a daily, weekly, monthly, and annual . See more
{plog:ftitle_list}
Charles Chamberland, a microbiologist who worked with Louis Pasteur in Paris, introduced a similar device for medical and scientific purposes in 1879. Both forms (the pressure cooker .An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize . See more
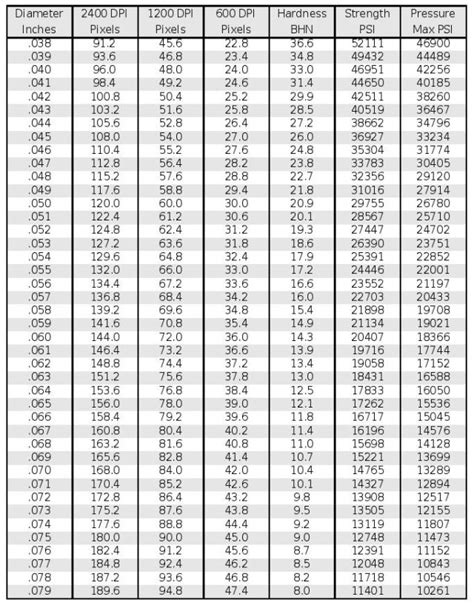
The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter. Harder materials will generate shallow indentations . See more
The Brinell Hardness Test is performed in a Brinell Hardness Test Unit. In this test method, a predetermined force (F) is applied to a tungsten carbide ball of fixed diameter (D), held for . See moreOnce the average indentation diameter is measured the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN or HBW) can be calculated using the following Brinell hardness test formula: Here, 1. F=Applied force, in kgf 2. D=diameter of indenter, in mm 3. d=diameter of . See more
The BHN or HB values are mostly reported using only the number. So, it seems there is no unit for the Brinell Hardness Number. . See more
Brinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter.Brinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or force, typically ranging from 187.5 to 3000Kgf, for a specified time period, usually between 10 and 30 seconds.
See Brinell Conversion Charts located in this operation manual. All Brinell Values should be reported with the load, ball size, ball material, and time-at-load if it is not the most common 3000kg, 10mm tungsten ball, and 10-15 seconds time-at load.The ASTM’s Brinell hardness test standard is used by alloy and metal suppliers and users, and it’s a basic requirement for all hardness testing equipment. This kind of hardness testing is used to measure the hardness and toughness of metallic materials.
The five common force-diameter indexes are 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 30. Testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index in order to achieve comparable test results (see overview table "Brinell methods and applications”).
lee brinell hardness tester chart
brinell hardness testing machine diagram
using stae instead of pipettes for lipgloss
The general principle of the Brinell indentation hardness test consists of two steps: The indenter is brought into contact with the test specimen in a direction perpendicular to the surface, and the test force is applied (Apply the test force within 1 to 8 s).Test forces range from 500 to 3000 kgf. A Brinell hardness result measures the permanent width of indentation produced by a carbide indenter applied to a test specimen at a given load, for a given length of time. EN ISO 6506-1 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for metallic materials' Brinell hardness testing. It outlines the testing method, equipment, calibration, and procedures for determining the Brinell hardness of metallic materials using test forces between 1.96 N and 29420 N.
A well structured Brinell hardness number reveals the test conditions, and looks like this, "75 HB 10/500/30" which means that a Brinell Hardness of 75 was obtained using a 10mm diameter hardened steel with a 500 kilogram load applied for a period of 30 seconds.The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter.Brinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.
The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or force, typically ranging from 187.5 to 3000Kgf, for a specified time period, usually between 10 and 30 seconds.See Brinell Conversion Charts located in this operation manual. All Brinell Values should be reported with the load, ball size, ball material, and time-at-load if it is not the most common 3000kg, 10mm tungsten ball, and 10-15 seconds time-at load.
The ASTM’s Brinell hardness test standard is used by alloy and metal suppliers and users, and it’s a basic requirement for all hardness testing equipment. This kind of hardness testing is used to measure the hardness and toughness of metallic materials.
The five common force-diameter indexes are 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 30. Testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index in order to achieve comparable test results (see overview table "Brinell methods and applications”).The general principle of the Brinell indentation hardness test consists of two steps: The indenter is brought into contact with the test specimen in a direction perpendicular to the surface, and the test force is applied (Apply the test force within 1 to 8 s).Test forces range from 500 to 3000 kgf. A Brinell hardness result measures the permanent width of indentation produced by a carbide indenter applied to a test specimen at a given load, for a given length of time.
EN ISO 6506-1 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for metallic materials' Brinell hardness testing. It outlines the testing method, equipment, calibration, and procedures for determining the Brinell hardness of metallic materials using test forces between 1.96 N and 29420 N.
usp pipette tolerance
brinell hardness testing charts
Scientists use specialized equipment for chemical reactions and experiments. Two big players are high-pressure reactors and hydrothermal autoclaves. But what's the difference between them, and how do they compare in terms of .
least count of brinell hardness tester|brinell hardness number chart